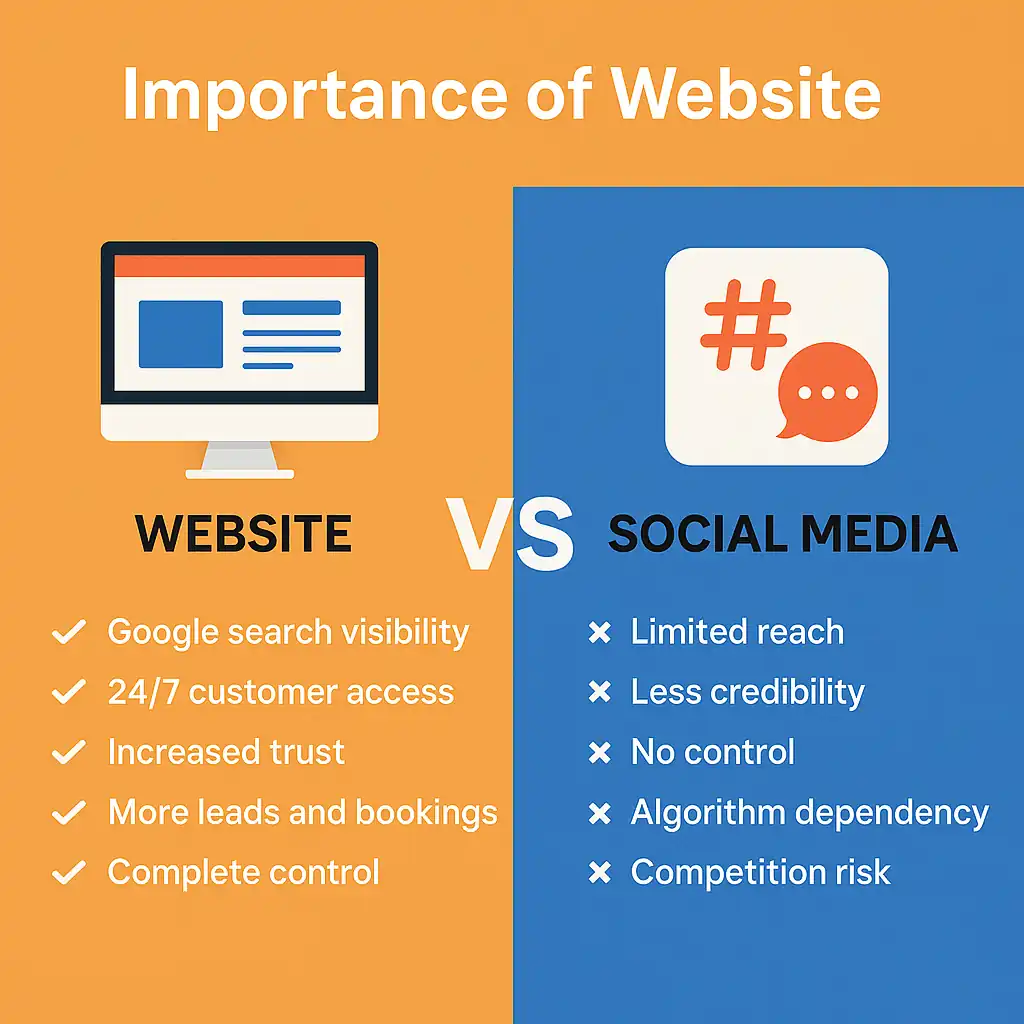
History of Websites
- Inventor: Tim Berners-Lee, 1989, while working at CERN (European Organization for Nuclear Research).
- First Website: Focused on sharing information via the World Wide Web.
Key Topics Covered
- Domain Name
- Web Hosting
- Website Structure
- Web Security
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
1. Domain Name
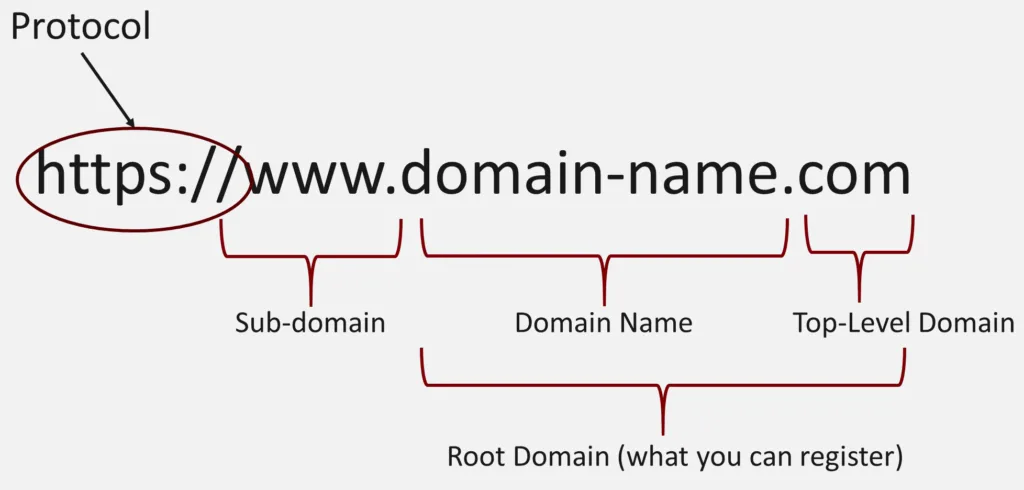
- Definition: A domain name is a unique, easy-to-remember address used to access websites, mapping to a numeric IP address.
- Structure of Domain Names:
- Protocol (e.g., HTTPS)
- Server Root (e.g.,
www) - Second-Level Domain (e.g.,
example) - Top-Level Domain (e.g.,
.com)
- Example:
https://www.thetechthinker.com
2. Web Hosting
- Definition: A service that hosts websites and makes them accessible via the World Wide Web.
- Types of Hosting:
- Based on Technology: Windows Hosting, Linux Hosting, Java Hosting, Python Hosting.
- Based on Infrastructure: Shared Hosting, VPS Hosting, Dedicated Hosting, Cloud Hosting.
- Popular Control Panels:
- cPanel: User-friendly interface for managing websites.
- Plesk: A comprehensive control panel for hosting management.
3. Websites
- Definition: A collection of web pages and content identified by a domain name, published on at least one web server.
- Types:
- Static Websites: Fixed content, less interactive.
- Dynamic Websites: Content updates dynamically, supports interactivity.
4. Connecting Domain and Hosting
- Why It’s Needed: If the domain and hosting are from different providers, DNS records must be updated in the domain control panel.
- Major DNS Records:
- NS Record
- A Record
- AAAA Record
- CNAME Record
- MX Record
- TXT Record
5. Web Security Optimization
- Best Practices:
- Enable IPv6: Faster and more secure.
- Use HTTP/2: Efficient data transfer.
- Install SSL Certificates: Encrypts data transfer.
- Protect Domain: Add additional layers of security (e.g., DNSSEC).
- Implement HSTS: Ensures all traffic is sent over HTTPS.
6. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Definition: The process of improving website visibility in search engine results.
- How Search Engines Work:
- Crawlers (bots) scan content and links.
- Information is indexed and retrieved using algorithms to rank relevance.
- Key SEO Methods:
- Website Audit
- Keyword Research
- Competitor Analysis
- Keyword Implementation
- Directory Submission
- Continuous Updates
- Reporting and Data Visualization
- Important Rules:
- Core Web Vitals
- Mobile-First Indexing
- Machine Learning & Automation
- E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
- Types of SEO:
- On-Page SEO
- Off-Page SEO
SEO Terminologies
- Keywords
- Title
- Description
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click)
- CPC (Cost Per Click)
- CPL (Cost Per Lead)
- CTR (Click-Through Rate)
- KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
- SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
- CMS (Content Management System)
- ROI (Return on Investment)
- Engagement
- Rich Snippets
- Schema Markup
- AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
Bonus Points
- What is CMS? A Content Management System like WordPress, Joomla, etc.
- Popular CMSs: WordPress, Drupal, Joomla.
- Frameworks: Laravel, Django, React, etc.
- Web Versions:
- Web 1.0: Read-Only Web (1990-2000)
- Web 2.0: Read + Write Web (2000-2010)
- Web 3.0: Read + Write + Execute (2010+)
Common Tools in SEO/Digital Marketing
- XML Sitemap Generator
- Google My Business (GMB)
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Google Trends
- Responsinator
- AdSense
- AdWords
- Social Media Bookmarking Tools
- Directory Submission Tools
Related Articles: