AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud: 7 Essential Parallel Comparison Insights for Startups & SMBs
AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud: Explore 7 parallel comparison insights—pricing, infrastructure, core services, security, and more—to pick the best cloud for startups & SMBs.
1. Pricing & Cost Comparison
Choosing between AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud often comes down to how each billing model aligns with your usage patterns and budget constraints. Misjudging this can lead to surprising overruns.
1.1 Pricing Model
-
AWS: Per‑second billing on EC2, Reserved Instances with up to 75% savings for 1–3 year commitments, and Spot Instances slashed up to 90%.
-
Azure: Pay‑as‑you‑go hourly rates, Reserved VM Instances offering up to 72% discounts, plus Azure Hybrid Benefit to reuse Windows Server licenses.
-
Google Cloud: Per‑second billing on Compute Engine, automatic Sustained‑use discounts up to 30%, and Preemptible VMs at up to 80% off ideal for batch jobs.
Key Take away:
Mix Reserved Instances with Spot/Preemptible VMs to cut costs on non-critical workloads.
Use Azure Hybrid Benefit if you already own Microsoft licenses.
Let GCP’s automatic discounts lower your baseline compute costs.
By strategically blending on‑demand and reserved capacities, a SaaS startup can ensure high availability while keeping costs predictable, for example, running the web tier on reserved instances and offloading analytics to preemptible VMs.
1.2 Free Tier & Credits
Early experimentation without financial risk is critical for startups validating product-market fit.
-
AWS: 12 months free tier (750 hrs/month t2.micro EC2, 5 GB S3, 750 hrs RDS micro) plus always‑free Lambda, DynamoDB, CloudWatch metrics.
-
Azure: $200 credit for 30 days, 12 months of free services (B1S VM, 250 GB SQL DB, 5 GB Blob Storage), and select always‑free services.
-
Google Cloud: $300 credit over 90 days, plus always‑free tier including one f1-micro VM, 5 GB Regional Storage, and 1 TB egress monthly.
Key Take away:
Prototype rolling updates via AWS free tier’s EC2 and Lambda.
Test Windows-based workloads under Azure’s $200 credit.
Validate microservices on GCP’s always‑free f1-micro instance.
Rolling your own CI pipeline or spinning up managed databases during this trial period lets you benchmark real-world performance and cost before committing.
2. Infrastructure & Performance
Global presence and network backbone quality directly affect user experience and SLA compliance.
2.1 Global Regions & Zones
Deploying nearest to your audience minimizes latency and boosts resilience.
-
AWS: 27 regions and 81 availability zones across six continents.
-
Azure: 60+ regions with paired zones for failover.
-
Google Cloud: 27 regions, 82 zones on Google’s private fiber network.
A fintech app handling sub-millisecond trades might choose an AWS region in Mumbai, whereas a video-streaming service could rely on GCP’s edge network for consistent throughput.
2.2 Networking & CDN
Reducing hops and offloading static content to edge caches accelerates page loads.
-
AWS: VPC with Direct Connect, CloudFront CDN in 200+ edge locations.
-
Azure: Virtual Network, ExpressRoute for private links, Azure CDN with integrated POPs.
-
Google Cloud: VPC peering, Cloud Interconnect, Cloud CDN leveraging Anycast.
Key Take away:
Offload static assets to CloudFront or Azure CDN to shave milliseconds off load times.
Use ExpressRoute or Direct Connect to secure high-throughput connections from on‑prem.
Enable GCP’s premium network tier for lowest jitter and packet loss.
Integrating a CDN can reduce global page-load times by up to 70%, a boost in user engagement that translates directly into retention and revenue.
3. Core Services
Your application’s backbone—compute, storage, and data—must balance performance, cost, and manageability.
3.1 Compute Services
Select the right mix of instance types and execution models.
-
AWS: EC2’s 300+ instance types, Lambda for serverless, ECS/EKS for container orchestration.
-
Azure: Virtual Machines (Linux/Windows), Functions for event-driven logic, AKS for Kubernetes.
-
Google Cloud: Compute Engine custom machine types, Cloud Functions, GKE for GCP-native Kubernetes.
Key Take away:
Auto‑scale web frontends with AWS Lambda’s pay-per-execution model.
Deploy hybrid workloads on Azure AKS connected to on‑prem via Azure Arc.
Standardize container platforms on GKE for portability.
A real‑time chat service can leverage AWS Lambda for message handling, while batch processing pipelines thrive on GKE’s autoscaling.
3.2 Storage Options
From hot data to deep archival, tiered storage optimizes cost-performance trade‑offs.
-
AWS: S3 Standard/Infrequent, EFS for shared files, Glacier Flexible/Retrieval for archives.
-
Azure: Blob Storage hot/cool/archive, Azure Files for SMB/NFS, Archive Storage for long‑term retention.
-
Google Cloud: Cloud Storage Standard to Archive, Filestore for high‑performance file shares.
Key Take away:
Implement lifecycle rules to move year-old logs from S3 Standard to Glacier.
Store compliance records in Azure Archive at ultra‑low costs.
Use GCP’s Coldline for cost-effective backup storage.
Automatic tiering reduces admin overhead, ensuring seldom‑accessed data doesn’t eat into your budget.
3.3 Databases & Analytics
Managed services free your team from routine maintenance and let you focus on insights.
-
AWS: RDS (MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server), DynamoDB NoSQL, Redshift data warehouse.
-
Azure: SQL Database serverless, Cosmos DB globally distributed NoSQL, Synapse Analytics.
-
Google Cloud: Cloud SQL managed RDBMS, Bigtable NoSQL, BigQuery for serverless OLAP.
Key Take away:
Run transactional workloads on RDS or Cloud SQL with minimal ops.
Scale globally with Cosmos DB’s multi‑region writes.
Analyze petabytes of data instantly in BigQuery.
Marketing teams analyzing campaign data will find BigQuery’s sub‑second response a game-changer compared to spinning up a self‑managed cluster.
4. Advanced Capabilities
These value-added services can differentiate your product and streamline operations.
4.1 AI/ML & Data Processing
Built‑in intelligence helps you derive actionable insights faster.
-
AWS: SageMaker for end‑to‑end ML, Rekognition for image/video analysis, EMR for Hadoop & Spark.
-
Azure: Azure Machine Learning with AutoML & MLOps, Cognitive Services vision/speech/language APIs, Synapse for unified analytics.
-
Google Cloud: Vertex AI unifies AutoML and custom training, Dataflow for stream/batch pipelines, Dataproc managed Hadoop/Spark.
Key Take away:
Prototype models in SageMaker Studio in minutes.
Add speech-to-text via Azure Cognitive Services with a few lines of code.
Build real-time ETL pipelines on Dataflow.
Healthcare startups could train diagnostic models on SageMaker, while retailers leverage Vertex AI to forecast demand.
4.2 Hybrid Cloud Support
Consistent operations across on‑prem and cloud reduce migration risk.
-
AWS: Outposts brings AWS hardware and APIs into your data center.
-
Azure: Azure Stack runs Azure services on-prem with full API compatibility.
-
Google Cloud: Anthos manages Kubernetes clusters across any environment.
Key Take away:
Keep sensitive data on-prem with AWS Outposts.
Run edge services on Azure Stack disconnected from the internet.
Orchestrate multi-cloud deployments with Anthos Config Management.
Enterprises in regulated industries can process data locally while leveraging the cloud for peak workloads.
5. Security & Compliance
Protecting customer data and meeting audit requirements is non‑negotiable.
5.1 Security Features
Each platform offers defense‑in-depth controls across identity, network, and data.
-
AWS: IAM roles & policies, KMS envelope encryption, Shield DDoS, WAF.
-
Azure: Azure AD for SSO/MFA, Key Vault for secrets, Defender for threat detection.
-
Google Cloud: IAM with predefined/custom roles, Cloud KMS, Security Command Center.
Key Take away:
Enforce least‑privilege access via IAM policies.
Store API keys securely in Key Vault or Cloud KMS.
Monitor anomalies with Security Command Center or Azure Sentinel.
Automate policy checks with native tools (AWS Config, Azure Policy, GCP Organization Policy) to reduce misconfigurations.
5.2 Compliance Standards
Out‑of‑the‑box certifications accelerate audits and compliance reporting.
-
AWS: ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, PCI DSS, HIPAA/HITRUST.
-
Azure: ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, HIPAA, GDPR, FedRAMP High.
-
Google Cloud: ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, HIPAA, GDPR, FIPS 140‑2.
Key Take away:
Download audit artifacts from AWS Artifact.
Track compliance posture in Azure Compliance Manager.
Use GCP’s Compliance Resource Center for regulatory mapping.
These resources let you pull evidence quickly, shaving days off audit prep.
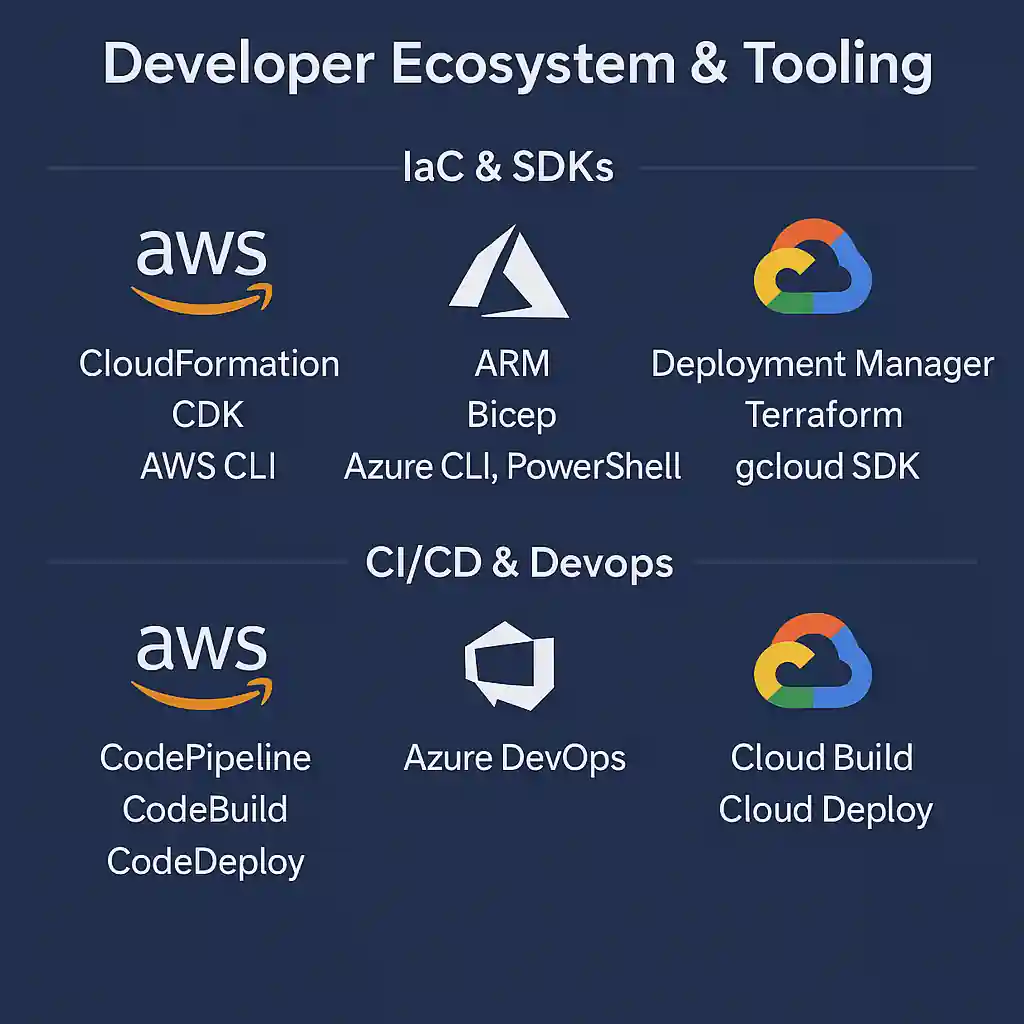
6. Developer Ecosystem & Tooling
A rich ecosystem of SDKs, CLIs, and automation tools boosts developer productivity.
6.1 IaC & SDKs
Define, deploy, and maintain infrastructure as code.
-
AWS: CloudFormation templates, CDK constructs, AWS CLI scripting.
-
Azure: ARM/Bicep templates, Azure CLI, PowerShell modules.
-
Google Cloud: Deployment Manager, Terraform modules, gcloud SDK.
Key Take away:
Version-control infra changes in Git alongside your application code.
Use CDK or Bicep for imperative/ declarative IaC preferences.
Standardize multi-cloud stacks with Terraform modules.
Embedding IaC into CI pipelines prevents drift and ensures reproducible environments.
6.2 CI/CD & DevOps
Automate your delivery lifecycle for reliability and speed.
-
AWS: CodePipeline orchestration, CodeBuild for tests, CodeDeploy for deployments.
-
Azure: Azure DevOps Services with Pipelines, Repos, Artifacts integrated.
-
Google Cloud: Cloud Build for builds, Cloud Deploy for progressive rollouts.
Key Take away:
Trigger pipelines on Git commit hooks.
Incorporate automated tests and security scans.
Use canary or blue/green deployments to reduce downtime.
Automating these workflows reduces manual toil and lets your team focus on features.
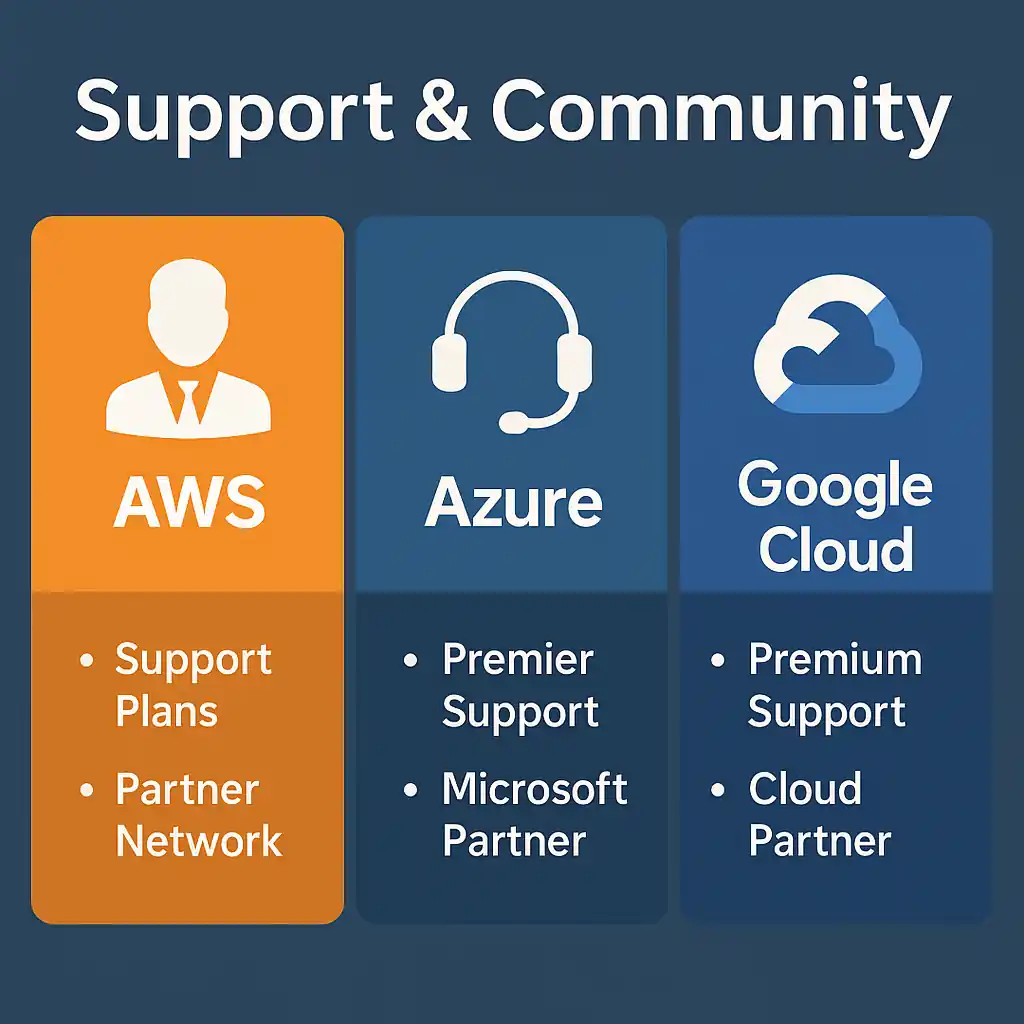
7. Support & Community
Responsive support plans and active communities are vital when issues arise.
-
AWS: Basic to Enterprise support plans, 90,000+ partners, annual re:Invent and local meetups.
-
Azure: Developer to Premier support tiers, 300,000+ Microsoft partners, Microsoft Ignite events.
-
Google Cloud: Standard to Premium support, growing partner network, Google Cloud Next conferences.
Key Take away:
Engage certified partners for architecture reviews.
Join Stack Overflow tags and provider forums for quick answers.
Attend user groups and hackathons to learn best practices.
Pairing official support with community resources ensures you never get stuck.
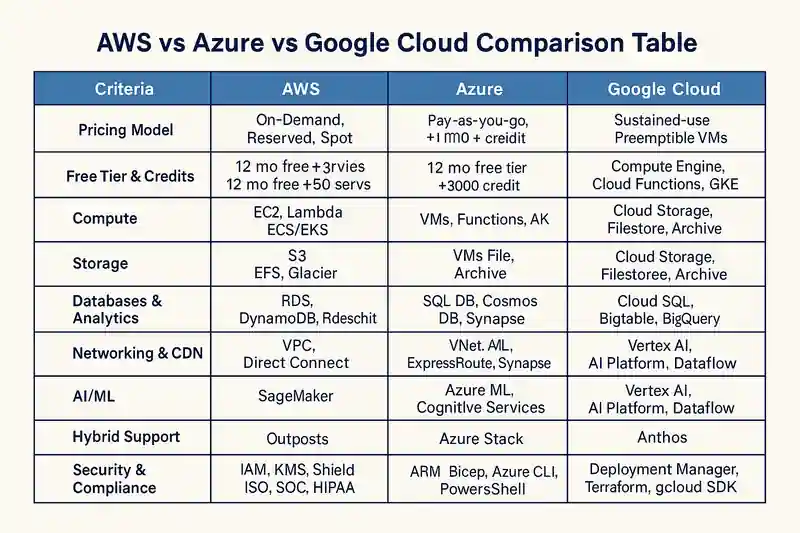
AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud Comparison Table
| Criteria | AWS | Azure | Google Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | On‑Demand, Reserved, Spot | Pay‑as‑you‑go, Reserved VMs, Hybrid Benefit | Sustained‑use discounts, Preemptible VMs |
| Free Tier & Credits | 12 mo free + always‑free services | 12 mo free + $200 credit | 12 mo free + $300 credit |
| Regions & Zones | 27 regions, 81 AZs | 60+ regions | 27 regions, 82 zones |
| Compute | EC2, Lambda, ECS/EKS | VMs, Functions, AKS | Compute Engine, Cloud Functions, GKE |
| Storage | S3, EFS, Glacier | Blob, File, Archive | Cloud Storage, Filestore, Archive |
| Databases & Analytics | RDS, DynamoDB, Redshift | SQL DB, Cosmos DB, Synapse | Cloud SQL, Bigtable, BigQuery |
| Networking & CDN | VPC, Direct Connect, CloudFront | VNet, ExpressRoute, Azure CDN | VPC, Cloud Interconnect, Cloud CDN |
| AI/ML | SageMaker, Rekognition, EMR | Azure ML, Cognitive Services, Synapse | Vertex AI, AI Platform, Dataflow |
| Hybrid Support | Outposts | Azure Stack | Anthos |
| Security & Compliance | IAM, KMS, Shield; ISO, SOC, HIPAA | AAD, Key Vault, Defender; ISO, SOC, HIPAA | IAM, Cloud KMS, Security Center; ISO, HIPAA |
| IaC & SDKs | CloudFormation, CDK, AWS CLI | ARM, Bicep, Azure CLI, PowerShell | Deployment Manager, Terraform, gcloud SDK |
| CI/CD & DevOps | CodePipeline, CodeBuild | Azure DevOps | Cloud Build, Cloud Deploy |
| Support & Community | Enterprise Tiers, Partner Network | Premier Support, Microsoft Partner | Premium Support, Google Cloud Partner |
Conclusion & Recommendation
By following this parallel comparison of AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud across seven critical dimensions—cost, infrastructure, core services, advanced features, security, tooling, and support—you can align your startup or SMB’s unique needs to the provider that delivers the most value.
Next Steps:
-
Sign up for free tiers and credits on all three clouds.
-
Run a proof-of-concept of your core workload and track cost, performance, and usability.
-
Match your final selection with your team’s existing skillsets and long-term roadmap.
-
Consult our Cloud Migration Strategies guide to plan a seamless cutover.
Armed with these insights, turning the “AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud” decision into a strategic advantage is now well within reach.
Read Also
- 11 Proven Factors: how to choose web hosting in 2025
- What is DNS?: Ultimate Guide to Domain Name System in 2025
- Best Web Hosting 2025 – Ultimate Guide to Fast, Secure & Reliable Providers
For more References
-
AWS Pricing – Official, up‑to‑date cost breakdowns for EC2, S3, RDS, Lambda, and more.
https://aws.amazon.com/pricing/ -
Microsoft Azure Pricing – Interactive calculator and detailed VM, storage, and network pricing.
https://azure.microsoft.com/pricing/ -
Google Cloud Pricing – Comprehensive rates for compute, storage, networking, plus sustained‑use discounts.
https://cloud.google.com/pricing -
AWS Well‑Architected Framework – Best practices and design principles to optimize cost, reliability, security, and performance.
https://aws.amazon.com/architecture/well-architected/ -
Google Cloud Architecture Framework – Guidelines and patterns for building secure, reliable, and efficient cloud solutions.
https://cloud.google.com/architecture/framework